Larave 6.0 Router 剖析
2个概念: router, route:
router是路由器, 操作的对象是route,route是保存具体的url路由关系,即什么url对应什么行为.
middleware to router
接上文的middleware,最终通过router->dispatch交给路由处理.
protected function dispatchToRouter()
{
return function ($request) {
$this->app->instance('request', $request);
return $this->router->dispatch($request);
};
}
2个动作:
public function dispatchToRoute(Request $request)
{
return $this->runRoute($request, $this->findRoute($request));
}
findRoute是找到request对应的route实例.
runRoute是执行route对应的action.
add route
在find run之前肯定要绑定,绑定就是Router::get ,Router::post这些方法干的活了:
Route::get('/post/{id}/{name?}', function(){..}});
Route::get('/post/{id}/{name?}', 'xxController@index');
Route::resource('/post/{id}/{name?}', 'xxController');
本质就是addRoute:
public function addRoute($methods, $uri, $action)
{
return $this->routes->add($this->createRoute($methods, $uri, $action));
}
创建route实例
包括method,uri,action等.
action就是路由对应的行为的抽象,可以是闭包,xxController@someWay,xxController(内含__invoke实现)等.
最终都想想尽办法调用到Controller类的方法,有显示方法直接调用方法,没有则调用1个callable对象,实在还不行会找
类的__invoke方法.
new Route里:
//D:\Projects\PHP\laravel\blog\vendor\laravel\framework\src\Illuminate\Routing\Route.php
public function __construct($methods, $uri, $action)
{
$this->uri = $uri;
$this->methods = (array) $methods;
//解析出最终可调用的action.
$this->action = $this->parseAction($action);
if (in_array('GET', $this->methods) && ! in_array('HEAD', $this->methods)) {
$this->methods[] = 'HEAD';
}
//action需要加prefix 类似/api/v2/post这种,则给uri加上prefix
if (isset($this->action['prefix'])) {
$this->prefix($this->action['prefix']);
}
}
new Route后,考虑到group操作,内层的路由可能需要合并上一层group的一些属性:
Route::group( ['prefix'=>'a', 'namespaces'=>'\\Top\\ClassA', 'where'=>''], function($router) {
Route::group(//more group...)
} )
namespace group后变成 \\Top\\ClassA\\ClassB\\Class\\C;
prefix group后变成 a.b.c;
where类似.
add保存
route add时添加到routes的collection对象:
/**
* An array of the routes keyed by method.
* 'get' = > [ 'url1'=> xxx, 'url2'=>xxx]
* 'post' = > [ 'url1'=> xxx, 'url2'=>xxx]
* @var array
*/
protected $routes = [];
/**
* A flattened array of all of the routes.
* [ 'get.url1'=> xxx,
'post.url2'=>xxx
...
]
* @var array
*/
protected $allRoutes = [];
/**命令路由
* A look-up table of routes by their names.
* ['name1'=>xxx, 'name2' =>xxx]
* @var array
*/
protected $nameList = [];
/**
* A look-up table of routes by controller action.
* ['url1'=>'xxController@index',
'url2'=> 'xxController@get'
]
* @var array
*/
protected $actionList = [];
添加到routes,allRoutes:
public function add(Route $route)
{
$this->addToCollections($route);
$this->addLookups($route);
return $route;
}
protected function addToCollections($route)
{
$domainAndUri = $route->getDomain().$route->uri();
foreach ($route->methods() as $method) {
$this->routes[$method][$domainAndUri] = $route;
}
$this->allRoutes[$method.$domainAndUri] = $route;
}
protected function addLookups($route)
{
// If the route has a name, we will add it to the name look-up table so that we
// will quickly be able to find any route associate with a name and not have
// to iterate through every route every time we need to perform a look-up.
if ($name = $route->getName()) {
$this->nameList[$name] = $route;
}
// When the route is routing to a controller we will also store the action that
// is used by the route. This will let us reverse route to controllers while
// processing a request and easily generate URLs to the given controllers.
$action = $route->getAction();
if (isset($action['controller'])) {
$this->addToActionList($action, $route);
}
}
数据长这样:
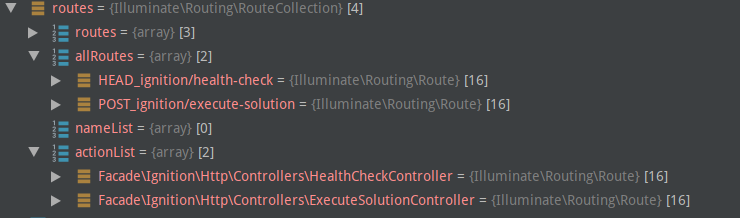
明白了上面的routes保存机制,也就明白为啥php artisan route:cache会加快速度了,api路由信息完全可从缓存里读,而不必每次都生成.
findRoute
请求为GET /post/1/cool时,如何才能匹配到上面的保存路由信息的结构routes里?
路由参数肯定要解析的.
//D:\Projects\PHP\laravel\blog\vendor\laravel\framework\src\Illuminate\Routing\Router.php
protected function findRoute($request)
{
//匹配的路由route对象
$this->current = $route = $this->routes->match($request);
//添加到IOC 容器.
$this->container->instance(Route::class, $route);
return $route;
}
//D:\Projects\PHP\laravel\blog\vendor\laravel\framework\src\Illuminate\Routing\RouteCollection.php
public function match(Request $request)
{
//根据GET POST这种取路由项,可能来自allRoutes or routes.
$routes = $this->get($request->getMethod());
// First, we will see if we can find a matching route for this current request
// method. If we can, great, we can just return it so that it can be called
// by the consumer. Otherwise we will check for routes with another verb.
$route = $this->matchAgainstRoutes($routes, $request);
if (! is_null($route)) {
return $route->bind($request);
}
// If no route was found we will now check if a matching route is specified by
// another HTTP verb. If it is we will need to throw a MethodNotAllowed and
// inform the user agent of which HTTP verb it should use for this route.
$others = $this->checkForAlternateVerbs($request);
if (count($others) > 0) {
return $this->getRouteForMethods($request, $others);
}
throw new NotFoundHttpException;
}
找到对应的路由项,还需要bind route参数,即post/{id}/对urlpost/1/的输入,意味着id=1.
public function bind(Request $request)
{
$this->compileRoute();
$this->parameters = (new RouteParameterBinder($this))
->parameters($request);
$this->originalParameters = $this->parameters;
return $this;
}
runRoute
接下来是具体的执行了。
protected function runRoute(Request $request, Route $route)
{
$request->setRouteResolver(function () use ($route) {
return $route;
});
$this->events->dispatch(new Events\RouteMatched($route, $request));
return $this->prepareResponse($request,
$this->runRouteWithinStack($route, $request)
);
}
runRouteWithinStack获得response,prepareResponse做最终的转化:
runRouteWithinStack
先过一遍middleware, 这里的中间件是路由里定义的routeMiddleware,不是系统级别的.
protected function runRouteWithinStack(Route $route, Request $request)
{
//disable的不要
$shouldSkipMiddleware = $this->container->bound('middleware.disable') &&
$this->container->make('middleware.disable') === true;
//route middleware加入
$middleware = $shouldSkipMiddleware ? [] : $this->gatherRouteMiddleware($route);
//熟悉的pipeline,就是处理middleware
return (new Pipeline($this->container))
->send($request)
->through($middleware)
->then(function ($request) use ($route) {
return $this->prepareResponse(
$request, $route->run()
);
});
}
真正的执行藏在$route->run()里:
public function run()
{
$this->container = $this->container ?: new Container;
try {
//action是 `XXController@method`的字符串
if ($this->isControllerAction()) {
return $this->runController();
}
//action是可执行函数的形式, `function method($a,$b){...}`
return $this->runCallable();
} catch (HttpResponseException $e) {
return $e->getResponse();
}
}
//action是1个可执行函数 , php 允许这样调用函数
/*
function test() { echo 'test';}
$name = 'test';
$name();
*/
protected function runCallable()
{
$callable = $this->action['uses'];
return $callable(...array_values($this->resolveMethodDependencies(
$this->parametersWithoutNulls(), new ReflectionFunction($this->action['uses'])
)));
}
再写controller方法的时候,可以注入路由参数id来使用:
public function index(Request $request, $id) {
}
其实就是实现了上面解析$id的过程.
背后稍微有点复杂了,在RouteDependencyResolverTrait里.
- RouteDependencyResolverTrait
核心方法就1个function resolveClassMethodDependencies(array $parameters, $instance, $method)
把instance的method 用到的参数(可能是对象,预先make出来)利用ReflectionMethod提取到parameters里.
调用这个函数的地方,正是传入的之前解析的路由参数:
public function dispatch(Route $route, $controller, $method)
{
$parameters = $this->resolveClassMethodDependencies(
//这个就是路由参数/post/{name}/{id}里的name,id
$route->parametersWithoutNulls(), $controller, $method
);
if (method_exists($controller, 'callAction')) {
return $controller->callAction($method, $parameters);
}
return $controller->{$method}(...array_values($parameters));
}
php sandbox: http://sandbox.onlinephpfunctions.com/code/c42bf20783c9c34b02ce0182b83155890d77a6c3
末了谈谈
route的灵活性
add route时,可以绑定Controller@index, Clousure, 甚至直接array, 或者model,但是为了这种灵活性,增加了不少代码,个人觉得没必要,其实就规定一种绑定方法的方式就好,无非就是多几行代码的区别.
//Closure
Route::get('/post/{id}', function(){...});
//Array with Closure, 会调用caller的闭包
Route::get('/post/{id}', ['id'=>xx. 'caller'= function(){...}]);
//Array
Route::get('/post/{id}', ['id'=>xx. 'content'=>xxx]);
//XXX实现了__invoke
Route::get('/post/{id}', new XXX::class);
//Model
\Models\Post $post;
Route::get('/post/{id}', $post);
//规定字符串,最常用的
Route::get('/post/{id}', 'PostController@index');
middleware
系统级,路由级,controller级.
再路由处理的时候,先不管系统定义的,路由级和controller级的需要合并处理:
路由级的middle是保存在route的action数组里:
'route'=>[ 'action'=>[ 'middleware'=>[...], ...]]
//D:\Projects\PHP\laravel\blog\vendor\laravel\framework\src\Illuminate\Routing\Route.php
public function gatherMiddleware()
{
if (! is_null($this->computedMiddleware)) {
return $this->computedMiddleware;
}
$this->computedMiddleware = [];
//marge unique
return $this->computedMiddleware = array_unique(array_merge(
$this->middleware(), $this->controllerMiddleware()
), SORT_REGULAR);
}
public function gatherRouteMiddleware(Route $route)
{
$middleware = collect($route->gatherMiddleware())->map(function ($name) {
return (array) MiddlewareNameResolver::resolve($name, $this->middleware, $this->middlewareGroups);
})->flatten();
//还要根据优先级排序
return $this->sortMiddleware($middleware);
}