设计模式 结构型模式 组合模式
组合模式
最好的例子就是操作系统里的文件夹的组织了. 删除某个根文件夹时, 所有子目录及文件也将删除,对使用者来讲,删除这个动作不关心删除的是文件夹(Composite)还是文件(Leaf);
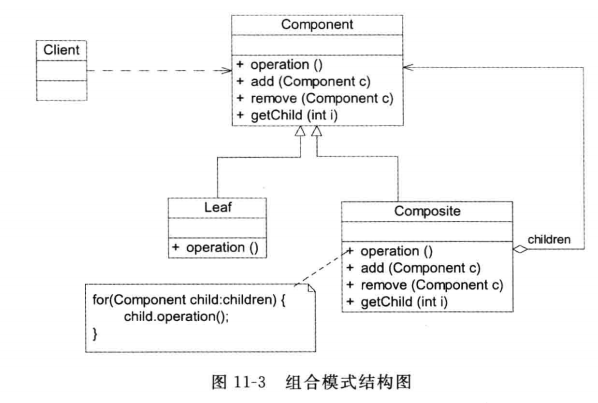
组合模式采用树形结构来实现普遍存在的对象容器,从而将“一对多”的关系转化“一对一”的关系,使得客户代码可以一致地处理对象和对象容器,无需关心处理的是单个的对象,还是组合的对象容器。
核心实现:
Component 既可代表叶子,也可以代表容器,客户端针对它编程,比如定义包含 Component 抽象构建类的容器对象如vector<Component> or map<id,Component>; 在 Compent 里,Add or Remove 可以针对单个叶结点(Leaf),也可以操作子树(Composite)。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <string.h> //itoa
#include <algorithm>
class Component {
public:
Component(std::string n = "default"): name(n){}
virtual ~Component(){}
virtual void add(const std::shared_ptr<Component> & c){}
//虚函数不可以重载
//virtual void add() ;
virtual void remove(){}
virtual void operation(){}
const std::string & getName() {return name;}
private:
std::string name;
};
class Leaf : public Component {
public:
Leaf(std::string n = "default in leaf" ) :Component(n) {}
~Leaf(){}
//~Leaf()= default;
void set_content(const std::string & s) {contents = s;}
void remove() {
std::cout << getName() << " removed !" << std::endl;
}
void operation() {
std::cout << "I am " << getName() << " " << contents << std::endl;
}
private:
std::string contents;
};
class Composite : public Component {
public:
Composite(std::string n = "default in composite" ) :Component(n) {}
~Composite(){}
void add(const std::shared_ptr<Component> & c) {
items.insert(std::make_pair(c->getName() ,c));
std::cout << getName() << " added " << c->getName() << std::endl;
}
void remove() {
//递归的remove items
for(auto it:items) {
it.second->remove();
//erase by key name
items.erase(it.first);
}
std::cout << getName() << " removed !" << std::endl;
}
void operation() {
if (items.empty() == 1)
std::cout << "Oper: empty dir" << std::endl;
else {
std::cout << "Oper: I am " << getName() << std::endl;
// same as remove
for(auto it:items) {
it.second->operation();
}
}
}
private:
std::map<std::string, std::shared_ptr<Component>> items;
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
auto root = new Composite("root");
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Composite>> dirs;
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<Leaf>> files;
for (unsigned long i = 0; i< 10 ; i ++) {
dirs.push_back(
std::make_shared<Composite>(std::string("dir")+std::to_string(i) )
);
files.push_back(
std::make_shared<Leaf>(std::string("file")+std::to_string(i) )
);
files[i]->set_content(std::string("Your lucky number is "+std::to_string(i)));
dirs[i]->add(files[i]);
}
root->add(dirs[0]);
root->add(dirs[1]);
dirs[0]->add(dirs[2]);
dirs[0]->add(dirs[3]);
dirs[0]->add(dirs[4]);
dirs[0]->add(dirs[5]);
dirs[1]->add(dirs[6]);
dirs[1]->add(dirs[7]);
dirs[1]->add(dirs[8]);
dirs[1]->add(dirs[9]);
std::cout << "Check all:" << std::endl;
root->operation();
std::cout << "Remove a branch:" << std::endl;
dirs[1]->remove();
std::cout << "Check again:" << std::endl;
root->operation();
std::cout << "Check removed branch:" << std::endl;
dirs[1]->operation();
return 0;
}
output:
dir0 added file0
dir1 added file1
dir2 added file2
dir3 added file3
dir4 added file4
dir5 added file5
dir6 added file6
dir7 added file7
dir8 added file8
dir9 added file9
root added dir0
root added dir1
dir0 added dir2
dir0 added dir3
dir0 added dir4
dir0 added dir5
dir1 added dir6
dir1 added dir7
dir1 added dir8
dir1 added dir9
Check all:
Oper: I am root
Oper: I am dir0
Oper: I am dir2
I am file2 Your lucky number is 2
Oper: I am dir3
I am file3 Your lucky number is 3
Oper: I am dir4
I am file4 Your lucky number is 4
Oper: I am dir5
I am file5 Your lucky number is 5
I am file0 Your lucky number is 0
Oper: I am dir1
Oper: I am dir6
I am file6 Your lucky number is 6
Oper: I am dir7
I am file7 Your lucky number is 7
Oper: I am dir8
I am file8 Your lucky number is 8
Oper: I am dir9
I am file9 Your lucky number is 9
I am file1 Your lucky number is 1
Remove a branch:
file6 removed !
dir6 removed !
file7 removed !
dir7 removed !
file8 removed !
dir8 removed !
file9 removed !
dir9 removed !
file1 removed !
dir1 removed !
Check again:
Oper: I am root
Oper: I am dir0
Oper: I am dir2
I am file2 Your lucky number is 2
Oper: I am dir3
I am file3 Your lucky number is 3
Oper: I am dir4
I am file4 Your lucky number is 4
Oper: I am dir5
I am file5 Your lucky number is 5
I am file0 Your lucky number is 0
Oper: empty dir
Check removed branch:
Oper: empty dir
- 透明模式和安全模式
透明方式:add,remove 等在 Component 中实现
安全方式,add,remove 等在 Composit 中实现
显然,上面的例子是安全模式.
如果想针对特殊派生类如 SomeLeaf or SomeComposite 做点什么, RTTI 是必不可少的.
if (typeid(some_variable ) == typeid(SomeLeaf) ) {
...
}